E-meal - A food delivery platform for seniors
Table of contents
- Elder-friendly
- Reliable
- Personalized
- Win-win-win
Why I chose this topic
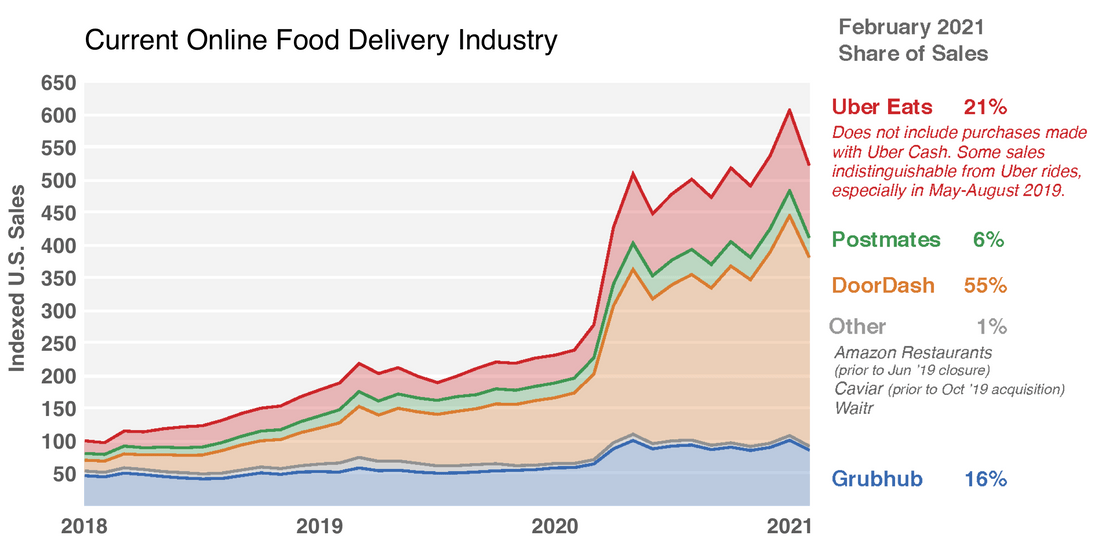
The online food delivery industry has doubled since the pandemic.
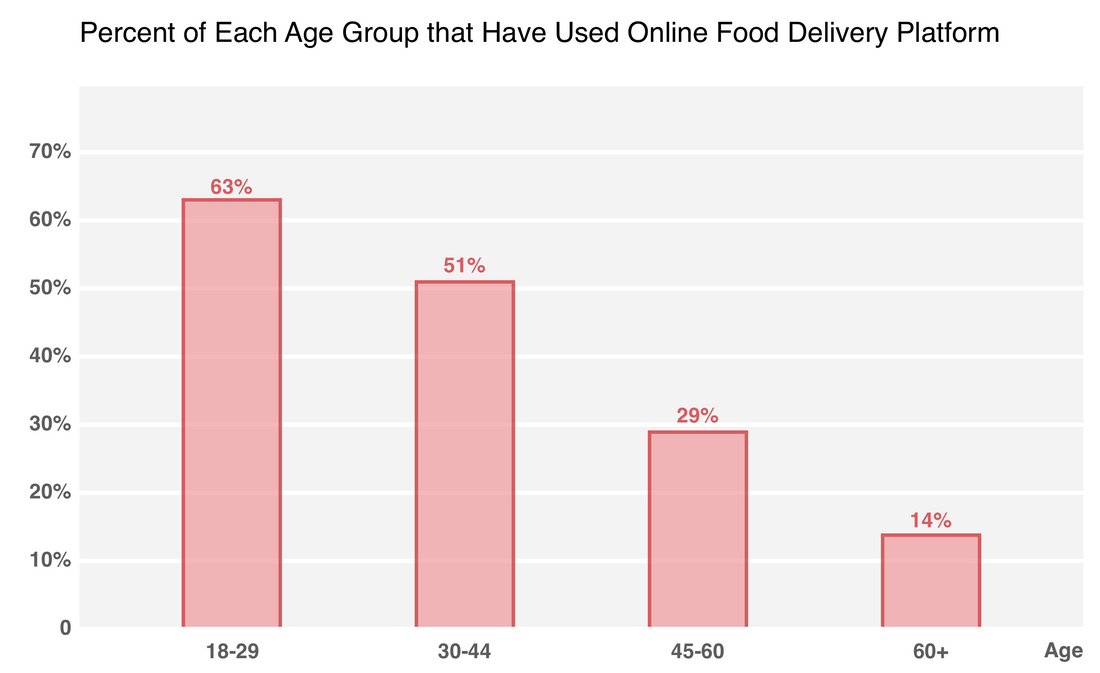
Only 14% of the senior group have tried online food platforms.
How I conducted my research
The second study is relationship building. The best way to understand how seniors behave is to contact the group that knows seniors best instead of contacting the target group directly. In my case, I collaborated with the Greater Boston Chinese Golden Age Center (GBCGAC) and gave technology lectures every week to get to know my target users and built trust with them. At the end of the lectures , I invited 5 of them to join my focus group to help test my proposal and iterate my prototypes.
The technology lecture I held in GBCGAC.
Focus group

We started our focus group discussion with their current food experience with Meals on Wheels (MOW). At the beginning of the pandemic, no one dared to go to the supermarket to buy groceries , so nutrition meals from MOW met their basic food needs. However, the monotonous menu hugely limited the variety of ingredients that were available to them, so they hope to learn how to use online platforms to order food. They also tried to order food by using Chowbus or Uber Eats, but gave up because they did not know how to create an account or a password or pay online.
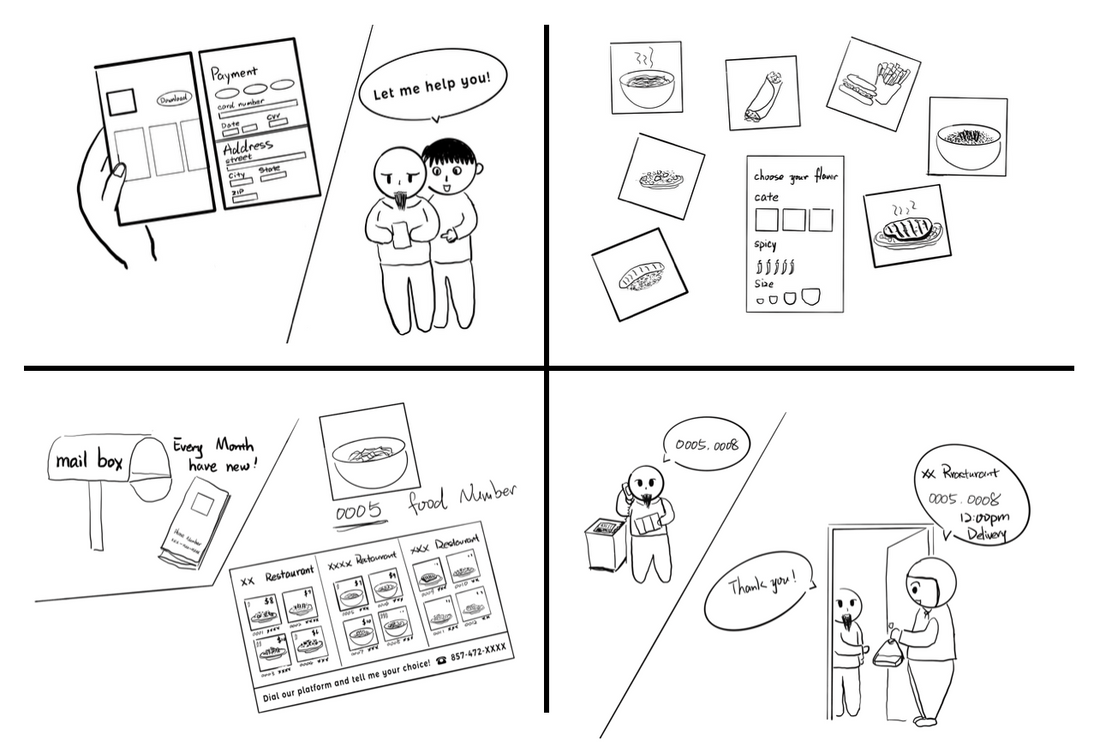
The storyboard I showed to the focus group, with the designing goal of:
- Reduce or avoid the need to use smart devices.
- Respect traditional ways of interaction (i.e. phone call).
- Make the food delivery experience more welcoming for seniors through recruiting couriers who are community members.
- Support local businesses through the sharing economy.
Service Blueprint
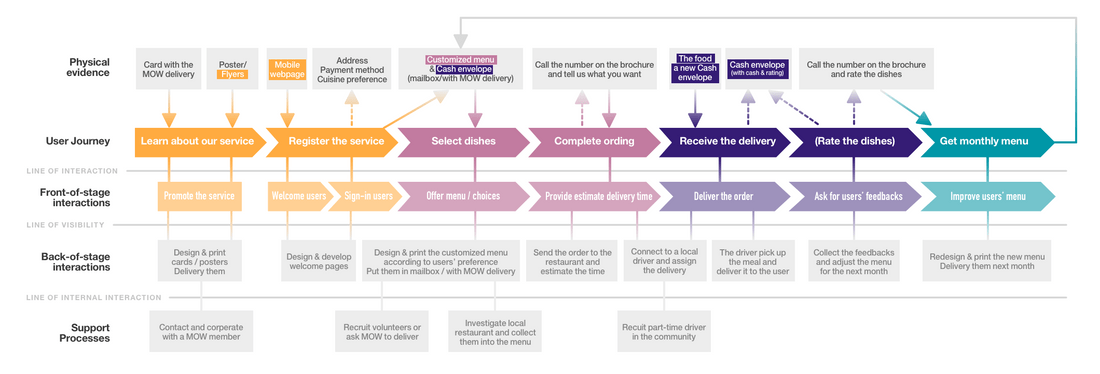
Based on feedback from the focus groups, my observation of seniors’ behaviors during the tech lectures, and previous research findings, I put together a blueprint for the platform. With this platform, seniors will not be not required to use smart devices after signing up, and they can also choose cash as their payment method.
This diagram has four different phases: onboarding , ordering , completing , and renewing . And also, there are four physical evidences in this system: flyer , mobile webpage , customized menu and cash envelope . The service blueprint follows the principles of being elder-friendly, reliable, personalized and win-win-win, which are concluded from the previous research.
What the final prototype looks like

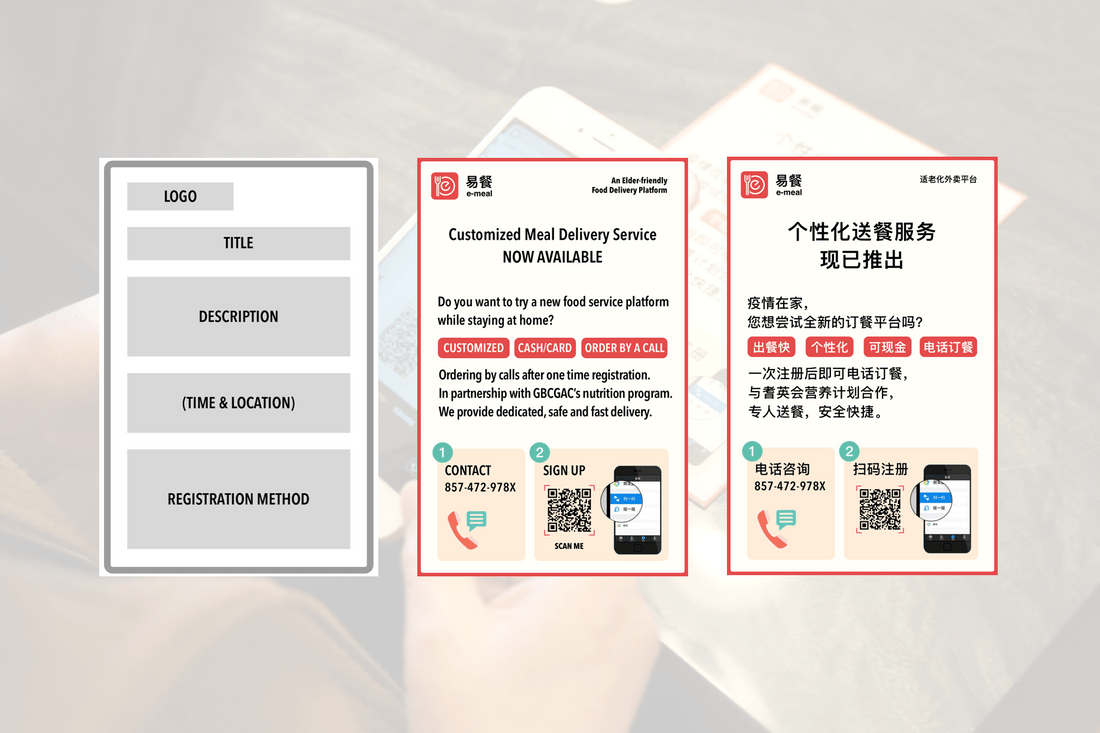
Flyer Users can call for inquiries or scan the code to open the website.

Mobile webpage Users can select food, courier and payment preference on the website. Users can also track and rate their orders after enjoying their meal.
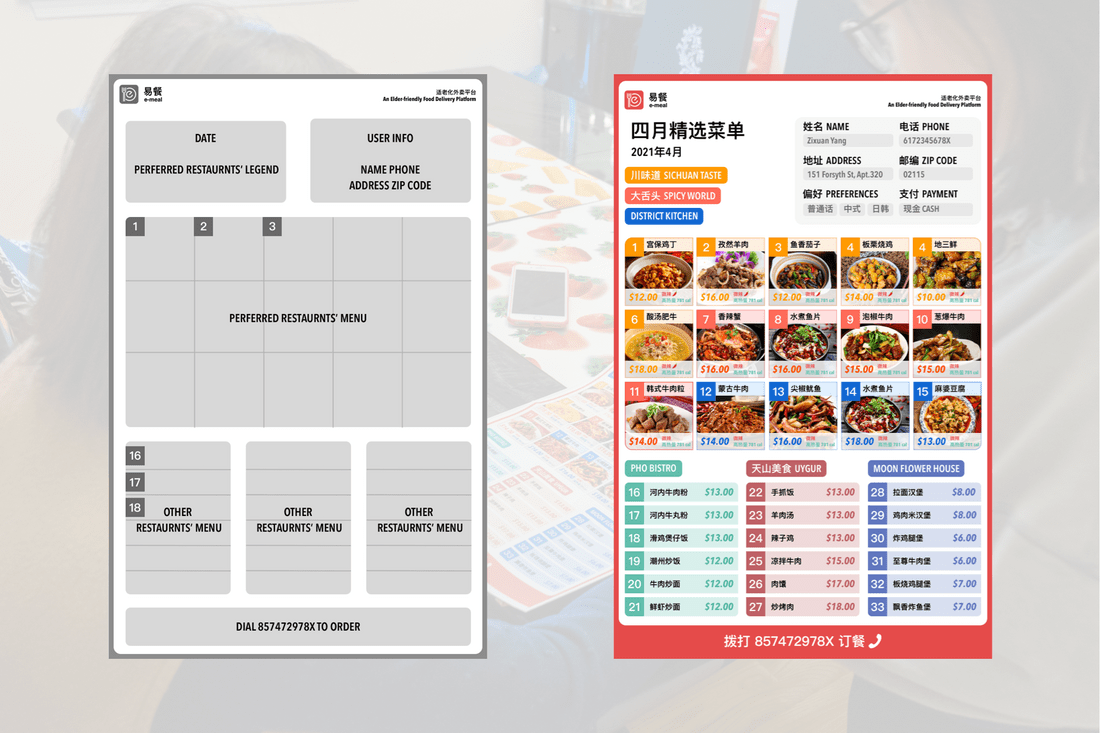
Customized menu It's customized for each user. Users can simply make an order by making a phone call and saying the dish's number.

Cash envelope Users can use this envelope to insert their cash payment and provide feedback by writing on the back side.
